Introduction
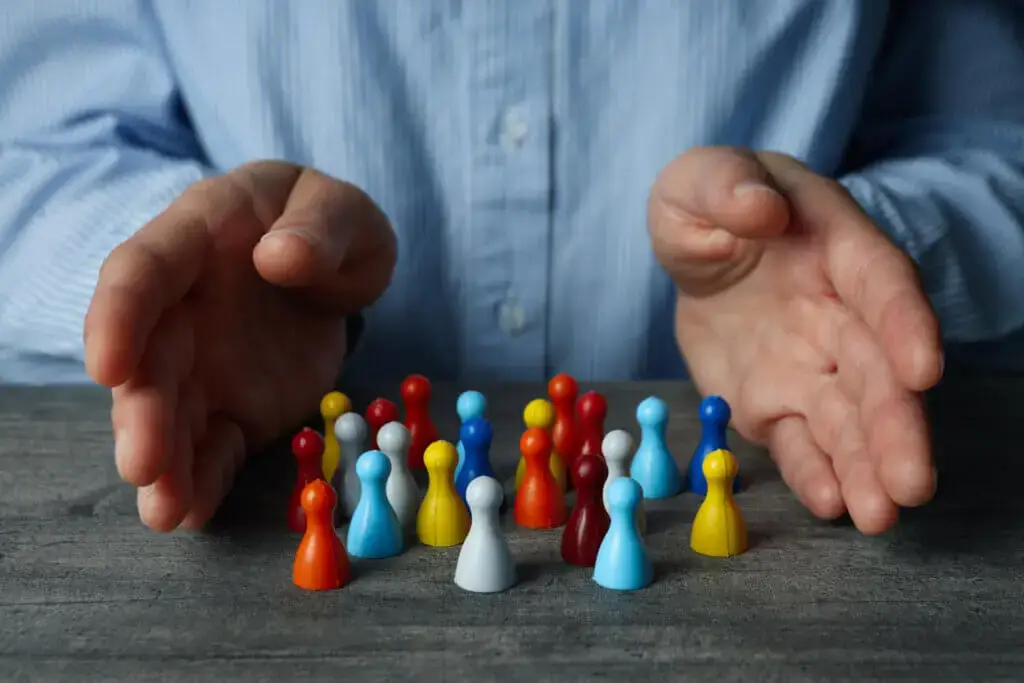
Successful businesses recognise that customer segmentation, where they cater to the diverse needs and preferences of their customer base, is paramount to sustainable growth and profitability.
Customer segmentation involves dividing your customer base into distinct groups based on shared characteristics such as demographics, behaviour, or purchasing patterns.
By segmenting customers, businesses can tailor their marketing efforts, product offerings, and customer experiences to better meet the needs of each group.
The result? Increased customer satisfaction, loyalty, and ultimately, revenue.
In this blog, we’ll delve into the intricacies of customer segmentation and explore how businesses can harness its power to drive revenue growth.
From identifying key customer segments to implementing targeted marketing strategies, we’ll uncover actionable insights to help you unlock the full profit potential of your business.
So, let’s dive in and discover how segmentation can transform your bottom line.
What is Customer Segmentation
Customer segmentation is a useful strategy in marketing. It involves taking customers and dividing them into specific groups based on similar characteristics.
This process allows businesses to better understand their customer base and tailor their marketing efforts to meet the specific needs and preferences of each segment.
Customer segmentation involves analysing various factors such as
- Demographics
- Psychographics
- Behavioural patterns, and
- Purchasing habits
to identify different groups within a target market.
By grouping customers with similar characteristics together, businesses can create more targeted and personalised marketing strategies.
For example, a clothing retailer might segment their customers based on factors such as
- Age
- Gender
- Income level, and
- Style preferences.
This segmentation allows the retailer to create specific marketing campaigns and product offerings tailored to different segments, such as creating a line of trendy clothing for young adults or offering discounts to budget-conscious shoppers.
The Importance of Understanding Customer Needs and Behaviours
Understanding customer needs and behaviours is crucial for businesses to effectively serve their target market.
Customer segmentation provides valuable insights into the diverse preferences, motivations, and purchasing habits of different customer groups.
By understanding the unique needs and behaviours of each segment, businesses can:
Tailor Products and Services
Customer segmentation enables businesses to develop products and services that cater to the specific preferences of different customer groups.
By offering personalised solutions, businesses can better meet the needs of their customers and increase customer satisfaction.
Optimise Marketing Strategies
Segmented marketing allows businesses to create targeted advertising campaigns that resonate with specific customer segments.
By delivering messages that are relevant and meaningful to each group, businesses can increase the effectiveness of their marketing efforts and improve ROI.
Enhance Customer Experience
By understanding customer behaviours and preferences, businesses can personalise the customer experience and provide tailored interactions at every touchpoint.
This could include offering personalised recommendations, providing targeted promotions, or optimising the user experience on digital platforms.
Maximise Profitability
Customer segmentation helps businesses identify high-value customer segments that are most profitable to target.
By focusing resources and efforts on these segments, businesses can maximise revenue and profitability.
In summary, customer segmentation is a valuable tool for businesses looking to understand and effectively serve their target market.
By dividing customers into distinct groups based on similar characteristics and understanding their unique needs and behaviours, businesses can create more targeted and personalised marketing strategies that drive customer engagement, satisfaction, and loyalty.
Types of Customers
New Customers: Attracting and Acquiring
Definition and Characteristics
“New Customers” refers to individuals or businesses who have recently started engaging with a company’s products or services.
These customers are in the early stages of their relationship with the business and have yet to establish a long-term connection.
Understanding the characteristics of new customers is essential for developing effective strategies to attract and acquire them.
Characteristics of new customers may include:
Lack of familiarity with the brand: New customers may have limited knowledge about the company, its products, or its reputation.
Limited engagement history: New customers may not have made any previous purchases or interactions with the business.
High potential for growth: New customers represent untapped potential for revenue growth and long-term loyalty if effectively engaged and retained.
Varied needs and preferences: New customers may have diverse needs, preferences, and expectations, requiring personalised approaches to attract and retain them.
Strategies for Attracting and Acquiring New Customers
Implementing effective strategies for attracting and acquiring new customers is crucial for business growth and sustainability.
Here are some key strategies:
Targeted Marketing Campaigns:
Utilise market research and segmentation techniques to identify and target specific customer segments with tailored marketing campaigns.
This could involve leveraging demographic, geographic, or psychographic data to create targeted messaging and promotions that resonate with the needs and preferences of new customers.
Offer Incentives and Promotions:
Offer incentives such as discounts, promotions, or special offers to incentivise new customers to make their first purchase or engage with the business.
These incentives can help attract new customers and encourage them to try out the company’s products or services.
Enhance Online Presence:
Invest in digital marketing channels such as social media, search engine optimisation (SEO), and content marketing to increase brand visibility and attract new customers online.
Ensure that your website is user-friendly, mobile-responsive, and optimised for search engines to attract organic traffic and capture the interest of new customers.
Leverage Referral Programs:
Encourage satisfied customers to refer their friends, family, or colleagues to your business through referral programs.
Offer incentives or rewards for successful referrals, such as discounts or freebies, to incentivise existing customers to spread the word and attract new customers.
Provide Exceptional Customer Service:
Deliver exceptional customer service to new customers to create a positive first impression and foster long-term loyalty.
Respond promptly to inquiries, address any concerns or issues promptly, and provide personalised support to make new customers feel valued and appreciated.
Create Engaging Content:
Develop high-quality, relevant content such as blog posts, articles, videos, or infographics that educates and entertains your target audience.
By creating engaging content that addresses the needs and interests of new customers, you can attract inbound traffic, establish credibility, and build trust with your audience.
By implementing these strategies, businesses can effectively attract and acquire new customers, ultimately driving growth, revenue, and long-term success.
Repeat Customers: Fostering Loyalty and Encouraging Repeat Business
Definition and Characteristics
Repeat customers are individuals or businesses who have previously purchased products or services from a company and choose to do so again.
These customers have already established a relationship with the business and have demonstrated loyalty by making multiple purchases or engaging with the company on a recurring basis.
Characteristics of repeat customers may include:
High level of satisfaction: Repeat customers are typically satisfied with their previous experiences with the company and perceive value in its products or services.
Trust and confidence: Repeat customers have developed trust and confidence in the brand, its offerings, and its ability to meet their needs and expectations.
Repeat purchasing behaviour: Repeat customers demonstrate a pattern of returning to the business for additional purchases or transactions, often becoming regular or loyal patrons.
Potential for advocacy: Repeat customers may become advocates for the brand, recommending it to friends, family, or colleagues based on their positive experiences.
Importance of Fostering Loyalty and Encouraging Repeat Business
Fostering loyalty and encouraging repeat business is crucial for the long-term success and sustainability of a company.
Here’s why:
Increased Revenue and Profitability:
Repeat customers represent a significant source of revenue and profitability for businesses.
They tend to spend more per transaction and are more likely to make additional purchases over time compared to new customers.
By fostering loyalty and encouraging repeat business, businesses can maximise revenue and profitability from their existing customer base.
Cost-Effectiveness:
Acquiring new customers can be costly and resource-intensive, involving expenses such as marketing, advertising, and promotional efforts.
In contrast, retaining existing customers is generally more cost-effective, as it requires less investment to maintain and nurture the relationship.
By focusing on retaining and satisfying existing customers, businesses can reduce customer acquisition costs and improve overall profitability.
Brand Advocacy and Referrals:
Satisfied repeat customers are more likely to become advocates for the brand, spreading positive word-of-mouth and recommending the company to others.
These loyal customers can play a crucial role in attracting new business through referrals, leading to a cycle of growth and expansion fuelled by customer advocacy.
Long-Term Relationships:
Building strong relationships with repeat customers fosters a sense of loyalty and commitment to the brand.
By consistently delivering exceptional products, services, and experiences, businesses can deepen the bond with their customers and establish long-term relationships that withstand competitive pressures and market fluctuations.
Feedback and Insights:
Repeat customers provide valuable feedback and insights that can help businesses improve their offerings, processes, and customer experience.
By actively soliciting feedback and listening to the needs and preferences of repeat customers, businesses can identify areas for improvement and innovation, ultimately enhancing customer satisfaction and loyalty.
In summary, fostering loyalty and encouraging repeat business is essential for businesses looking to achieve sustainable growth, profitability, and success in today’s competitive marketplace.
By prioritising the needs and preferences of repeat customers and delivering exceptional value and experiences, businesses can build strong relationships, drive revenue, and secure a loyal customer base for the long term.
Loyal Customers: Building and Maintaining Customer Loyalty
Definition and Characteristics
Loyal customers are individuals or businesses who consistently choose to engage with a specific company’s products or services over an extended period.
These customers demonstrate a strong affinity and commitment to the brand, often returning for repeat purchases and advocating for the company to others.
Characteristics of Loyal Customers May Include:
Consistent patronage: Loyal customers repeatedly choose to do business with the company, often preferring its offerings over competitors.
Emotional attachment: Loyal customers feel a sense of emotional connection and loyalty towards the brand, based on positive experiences, trust, and shared values.
Advocacy and referrals: Loyal customers are more likely to recommend the company to friends, family, or colleagues based on their positive experiences, leading to word-of-mouth referrals and new business opportunities.
Higher lifetime value: Loyal customers tend to have a higher lifetime value to the company, as they are more likely to make repeat purchases, spend more per transaction, and remain customers for an extended period.
Strategies for Building and Maintaining Customer Loyalty
Building and maintaining customer loyalty requires a strategic and proactive approach focused on delivering exceptional value, experiences, and service.
Here are some key strategies:
Deliver Consistent Quality:
Consistently deliver high-quality products, services, and experiences that meet or exceed customer expectations.
Consistency is crucial for building trust and confidence in the brand and fostering long-term loyalty among customers.
Personalise the Experience:
Tailor the customer experience to individual preferences and needs by collecting and leveraging customer data and insights.
Personalisation can involve customising product recommendations, offering personalised promotions or discounts, and providing personalised communication and support.
Reward Loyalty:
Implement a customer loyalty program to reward and incentivise repeat purchases and engagement.
Offer rewards such as discounts, exclusive access, or loyalty points that can be redeemed for future purchases.
Recognising and rewarding loyal customers helps reinforce their loyalty and encourages continued patronage.
Provide Exceptional Customer Service:
Deliver exceptional customer service at every touchpoint, including pre-sale, post-sale, and support interactions.
Go above and beyond when interacting with clients. Make sure you respond as quick as possible to enquiries and concerns. If there are any issues then resolve as quickly as possible.
Positive customer service experiences can strengthen the bond with customers and enhance loyalty.
Build Emotional Connections:
Foster emotional connections with customers by creating memorable experiences, telling compelling stories, and aligning with shared values and beliefs.
Engage customers on an emotional level through storytelling, community-building initiatives, and cause-related marketing efforts that resonate with their values and aspirations.
Solicit and Act on Feedback:
Actively solicit feedback from customers and use it to continuously improve products, services, and the overall customer experience.
Demonstrate that you value customer input by incorporating their suggestions, addressing their concerns, and making meaningful changes based on their feedback.
Engaging customers in the feedback process shows that their opinions matter and strengthens the relationship.
By implementing these strategies, businesses can effectively build and maintain customer loyalty, creating a loyal customer base that drives long-term growth, profitability, and success.
Impulse Buyers: Capturing Spontaneous Purchases
Definition and Characteristics
Impulse buyers are individuals who make unplanned or spontaneous purchases based on sudden desires or impulses, rather than careful consideration or premeditation.
These customers are often influenced by factors such as emotions, convenience, or visual stimuli, leading them to make impulsive buying decisions.
Characteristics of impulse buyers may include:
Spontaneous purchasing behaviour: Impulse buyers tend to make purchases on the spur of the moment, without extensive deliberation or research.
Emotional triggers: Impulse buyers are often influenced by emotions such as excitement, curiosity, or desire, which drive their purchasing decisions.
Low resistance to temptation: Impulse buyers may have a tendency to succumb to temptation when presented with appealing products, promotions, or incentives.
Variety-seeking behaviour: Impulse buyers may be drawn to novelty or unique offerings, seeking out new and interesting products or experiences.
Approaches for Capturing Impulse Purchases and Maximising Sales Opportunities
Capturing impulse purchases requires strategic approaches designed to capitalise on spontaneous buying behaviour and create opportunities for upselling and cross-selling.
Here are some key approaches:
Strategic Product Placement:
Place high-margin or impulse items in prominent locations within the store or on the website to maximise visibility and exposure.
Position these items near checkout counters, entranceways, or high-traffic areas where customers are more likely to notice them and make impulse purchases.
Create Visual Appeal:
Use eye-catching displays, signage, and packaging to attract the attention of impulse buyers and stimulate their interest.
Incorporate vibrant colours, bold graphics, and compelling imagery to make products stand out and entice customers to make spontaneous purchases.
Limited-time Offers and Promotions:
Create a sense of urgency and scarcity by offering limited-time promotions, discounts, or exclusive deals that encourage impulse buyers to act quickly.
Highlight the time-sensitive nature of the offer to create a sense of FOMO (fear of missing out) and motivate customers to make immediate purchases.
Bundle and Cross-sell:
Bundle complementary products together or offer cross-selling suggestions to encourage impulse buyers to add additional items to their purchase.
Highlight the value or convenience of purchasing multiple items together, and offer incentives such as discounts or freebies to sweeten the deal and drive incremental sales.
Convenience and Accessibility:
Make it easy for impulse buyers to complete their purchase by streamlining the checkout process and offering convenient payment options such as mobile payments or one-click ordering.
Minimise friction and remove barriers to purchase to capitalise on spontaneous buying impulses.
Engage Emotions and Experiences:
Appeal to the emotions and senses of impulse buyers by creating immersive and engaging shopping experiences.
Use storytelling, demonstrations, or interactive displays to evoke emotions and create memorable moments that inspire impulse purchases.
By implementing these approaches, businesses can effectively capture impulse purchases and maximise sales opportunities, driving revenue and profitability through spontaneous buying behaviour.
Bargain Hunters: Meeting the Needs of Price-Sensitive Customers
Definition and Characteristics
Bargain hunters are customers who prioritise finding the best deals, discounts, and bargains when making purchasing decisions.
These customers are highly price-sensitive and actively seek out opportunities to save money, whether through sales, promotions, or discounts.
Bargain hunters are motivated by the desire to get the most value for their money and may be willing to switch brands or retailers to find the best deals.
Characteristics of bargain hunters may include:
Price sensitivity: Bargain hunters are particularly sensitive to price fluctuations and are constantly on the lookout for discounts or cost-saving opportunities.
Comparison shopping: Bargain hunters often engage in extensive research and comparison shopping to find the best prices and deals before making a purchase.
Value-consciousness: Bargain hunters prioritise value over brand loyalty and are willing to sacrifice brand prestige or features in favour of lower prices.
Patience and persistence: Bargain hunters are willing to invest time and effort into finding the best deals, whether through online searches, coupon clipping, or waiting for sales events.
Tactics for Catering to Price-Sensitive Customers While Maintaining Profitability
Meeting the needs of price-sensitive customers requires strategic approaches that balance the goal of attracting value-conscious shoppers with the need to maintain profitability and sustainability.
Here are some tactics for catering to price-sensitive customers while preserving profitability:
Offer Discounts and Promotions:
Implement regular discounts, sales, and promotions to appeal to price-sensitive customers and incentivise purchases.
Offer limited-time deals, flash sales, or clearance events to create a sense of urgency and encourage immediate action.
Price Matching Guarantee:
Provide a price matching guarantee to assure customers that they are getting the best deal available.
Match competitors’ prices or offer to refund the price difference if customers find a lower price elsewhere, helping to instil confidence and trust in the brand.
Value Bundles and Packages:
Create value-oriented bundles or packages that combine multiple products or services at a discounted price.
By offering bundled pricing, businesses can increase the perceived value of their offerings while providing savings to price-sensitive customers.
Loyalty Programs and Rewards:
Implement a customer loyalty program that rewards repeat purchases and engagement with discounts, points, or exclusive offers.
Encourage repeat business from price-sensitive customers by providing incentives for loyalty and repeat purchases.
Transparent Pricing and Clear Communication:
Be transparent about pricing and communicate value effectively to price-sensitive customers.
Clearly display prices, discounts, and savings opportunities to help customers make informed purchasing decisions and avoid surprises at checkout.
Focus on Cost Efficiency:
Streamline operations and optimise costs to maintain profitability while offering competitive prices to price-sensitive customers.
Identify areas where costs can be reduced without sacrificing quality or customer experience, such as optimising supply chain logistics or negotiating better terms with suppliers.
By implementing these tactics, businesses can effectively cater to price-sensitive customers while maintaining profitability and sustainability in the competitive marketplace.
Balancing the needs of value-conscious shoppers with the financial goals of the business is essential for long-term success and growth.
High-Value Customers: Prioritising Personalised Service and Retention
Definition and Characteristics
High-value customers are individuals or businesses who contribute significant revenue, profitability, and long-term value to a company.
These customers go beyond making occasional purchases and instead demonstrate a consistent pattern of high spending, loyalty, and engagement with the brand.
High-value customers are instrumental in driving revenue growth, profitability, and sustainability for businesses.
Characteristics of high-value customers may include:
High spending: High-value customers consistently make significant purchases or transactions with the company, contributing to a large portion of its revenue and profitability.
Repeat business: High-value customers demonstrate loyalty and commitment to the brand by making repeat purchases over time, often becoming regular or repeat patrons.
Lifetime value: High-value customers have a high lifetime value to the company, as they are more likely to make repeat purchases, spend more per transaction, and remain customers for an extended period.
Engagement and advocacy: High-value customers actively engage with the brand, providing valuable feedback, referrals, and advocacy that contribute to the company’s success and growth.
Strategies for Identifying and Prioritising High-Value Customers for Personalised Service and Retention
Identifying and prioritising high-value customers is essential for delivering personalised service, fostering loyalty, and maximising retention.
Here are some strategies for identifying and prioritising high-value customers:
Data Analysis and Segmentation:
Utilise customer data and analytics to identify patterns, trends, and behaviours that indicate high-value customers.
Segment customers based on factors such as spending levels, purchase frequency, recency, and engagement to identify the most valuable segments.
RFM Analysis:
Conduct RFM (Recency, Frequency, Monetary) analysis to identify high-value customers based on their recent purchase activity, frequency of purchases, and total monetary value spent.
Prioritise customers who have made recent, frequent, and high-value purchases for personalised service and retention efforts.
Customer Lifetime Value (CLV) Modeling:
Calculate and analyse customer lifetime value (CLV) to identify high-value customers who are likely to generate the most revenue and profitability over their lifetime.
Focus on retaining and cultivating relationships with high-CLV customers to maximise long-term value.
Behavioural Segmentation:
Segment customers based on behavioural indicators such as browsing behaviour, engagement with marketing campaigns, and interactions with the brand across various channels.
Prioritise customers who exhibit behaviours indicative of high engagement and loyalty for personalised service and retention efforts.
Personalised Communication and Offers:
Tailor communication and offers to high-value customers based on their preferences, interests, and past purchase history.
Provide personalised recommendations, exclusive offers, and VIP experiences to make high-value customers feel valued and appreciated.
Dedicated Account Management:
Assign dedicated account managers or customer service representatives to high-value customers to provide personalised support, assistance, and guidance.
Build strong relationships with high-value customers by offering proactive assistance, addressing their needs and concerns promptly, and going above and beyond to exceed their expectations.
By implementing these strategies, businesses can effectively identify and prioritise high-value customers for personalised service and retention efforts, ultimately driving loyalty, satisfaction, and long-term profitability.
Investing in the retention and satisfaction of high-value customers is critical for maximising revenue and sustaining growth in today’s competitive marketplace.
Browsing Customers: Engaging and Converting Potential Buyers
Definition and Characteristics
Browsing customers are individuals who visit a company’s website, store, or platform to explore products or services without necessarily making immediate purchases.
These customers may be in the early stages of their purchasing journey, conducting research, comparing options, or simply browsing out of curiosity.
Understanding the characteristics of browsing customers is essential for effectively engaging them and converting them into buyers.
Characteristics of browsing customers may include:
Curiosity and exploration: Browsing customers are motivated by curiosity and a desire to explore available options, features, and offerings.
Information gathering: Browsing customers may be researching products, comparing prices, reading reviews, or seeking information to inform their purchasing decisions.
Indecisiveness: Browsing customers may be undecided or hesitant about making a purchase, requiring additional information or persuasion to convert.
Variable intent: Browsing customers may have varying levels of intent to purchase, ranging from casual browsing to serious consideration of buying.
Strategies for Engaging Browsing Customers and Converting Them into Buyers
Engaging browsing customers and converting them into buyers requires strategic approaches that capture their interest, provide relevant information, and encourage action.
Here are some strategies for engaging browsing customers and guiding them towards making a purchase:
Optimise User Experience:
Ensure that your website, store, or platform offers a user-friendly and intuitive browsing experience.
Make it easy for browsing customers to navigate, search for products, and access relevant information such as product descriptions, specifications, and reviews.
Visual Merchandising:
Use visually appealing displays, images, and multimedia content to showcase products and capture the attention of browsing customers.
Highlight key features, benefits, and use cases to pique their interest and encourage further exploration.
Provide Detailed Product Information:
Offer comprehensive product information, including detailed descriptions, specifications, dimensions, and pricing.
Address common questions and concerns that browsing customers may have to provide clarity and instil confidence in their purchasing decision.
Offer Interactive Features:
Incorporate interactive features such as product configurators, virtual try-on tools, or live chat support to engage browsing customers and provide personalised assistance.
Enable customers to interact with products in meaningful ways to enhance their shopping experience and facilitate decision-making.
Recommendation Engines:
Implement recommendation engines or personalised product recommendations based on browsing history, preferences, and behaviour.
Suggest relevant products or complementary items that align with the interests and needs of browsing customers to encourage upselling and cross-selling opportunities.
Incentivise Action:
Offer incentives or promotions to encourage browsing customers to take action and make a purchase.
Provide limited-time offers, discounts, or exclusive deals to create a sense of urgency and motivate browsing customers to convert.
Capture Contact Information:
Capture contact information such as email addresses or phone numbers from browsing customers to follow up with targeted marketing campaigns and remarketing efforts.
Stay engaged with browsing customers through email newsletters, retargeting ads, or personalised offers to nurture leads and encourage conversions over time.
By implementing these strategies, businesses can effectively engage browsing customers and guide them towards making informed purchasing decisions, ultimately driving conversions and increasing sales.
Creating a seamless and compelling browsing experience is essential for capturing the interest and loyalty of potential buyers in today’s competitive marketplace.
Needs-Based Customers: Understanding and Fulfilling Specific Needs
Definition and Characteristics
Needs-based customers are individuals or businesses whose purchasing decisions are primarily driven by specific needs, requirements, or problems they aim to address.
These customers prioritise finding solutions that effectively fulfil their needs and satisfy their objectives, rather than being influenced solely by brand loyalty or extraneous factors.
Characteristics of needs-based customers may include:
Problem-solving mindset: Needs-based customers approach the purchasing process with a focus on finding solutions to specific challenges, issues, or requirements they encounter.
Research-oriented behaviour: Needs-based customers engage in thorough research and evaluation of available options to identify products or services that best meet their needs and expectations.
Value-driven decision-making: Needs-based customers prioritise value and functionality over brand recognition or status, seeking products or services that offer the most practical and cost-effective solutions.
Flexibility and adaptability: Needs-based customers may be open to exploring alternative or unconventional solutions if they better address their specific needs or preferences.
Importance of Understanding and Fulfilling the Specific Needs of Needs-Based Customers
Understanding and fulfilling the specific needs of needs-based customers is essential for building trust, satisfaction, and loyalty, as well as driving long-term success for businesses.
Here’s why:
Customer Satisfaction and Loyalty:
By addressing the specific needs and requirements of needs-based customers, businesses can deliver solutions that genuinely meet their expectations and provide tangible value.
This leads to increased customer satisfaction and loyalty, as needs-based customers are more likely to return for future purchases and recommend the business to others.
Differentiation and Competitive Advantage:
Understanding the unique needs of needs-based customers allows businesses to differentiate themselves from competitors by offering tailored solutions that address specific pain points or challenges.
By focusing on fulfilling unmet needs, businesses can carve out a niche in the market and establish a competitive advantage.
Market Opportunity and Growth:
Needs-based customers represent a significant market opportunity for businesses, as they actively seek out solutions to specific problems or requirements.
By catering to the needs of this customer segment, businesses can tap into new markets, expand their customer base, and drive revenue growth.
Customer-Centric Innovation:
Understanding the specific needs of needs-based customers enables businesses to innovate and develop products or services that directly address those needs.
By listening to customer feedback, conducting market research, and staying attuned to evolving trends, businesses can continuously adapt and improve their offerings to better serve their target audience.
Positive Brand Perception:
By consistently fulfilling the specific needs of needs-based customers, businesses can build a positive brand reputation and perception as a trusted provider of solutions.
This enhances brand credibility, fosters goodwill, and strengthens the relationship between the business and its customers.
In summary, understanding and fulfilling the specific needs of needs-based customers is crucial for driving customer satisfaction, loyalty, and growth.
By prioritising customer needs and delivering tailored solutions, businesses can position themselves for long-term success in today’s competitive marketplace.
Unhappy Customers: Addressing and Resolving Issues
Definition and Characteristics
Unhappy customers are individuals who have had negative experiences with a company’s products, services, or interactions, leading to dissatisfaction and discontent.
These customers may have encountered issues such as poor product quality, unsatisfactory customer service, delayed deliveries, or billing errors, resulting in frustration and disappointment.
Characteristics of unhappy customers may include:
Expressions of dissatisfaction: Unhappy customers may express their dissatisfaction through complaints, negative reviews, or social media posts highlighting their negative experiences.
Loss of trust: Unhappy customers may lose trust in the company’s ability to meet their needs or provide satisfactory solutions, leading to a breakdown in the customer-company relationship.
Potential for churn: Unhappy customers may be at risk of discontinuing their relationship with the company, switching to competitors, or spreading negative word-of-mouth, which can harm the company’s reputation and bottom line.
Strategies for Addressing and Resolving Issues to Turn Unhappy Customers into Satisfied Ones
Addressing and resolving issues with unhappy customers requires prompt action, empathy, and a commitment to finding satisfactory solutions.
Here are some strategies for effectively addressing and resolving issues to turn unhappy customers into satisfied ones:
Listen and Empathise:
Listen attentively to the concerns and grievances of unhappy customers, acknowledging their frustrations and demonstrating empathy for their situation.
Show genuine concern and understanding for their perspective, validating their feelings and experiences.
Apologise and Take Responsibility:
Offer a sincere apology for any inconvenience or dissatisfaction experienced by the customer, taking responsibility for the issues they encountered.
Accept accountability for any mistakes or shortcomings on the part of the company, and express a genuine commitment to resolving the issue promptly.
Resolve the Issue Proactively:
Take immediate action to address the customer’s concerns and resolve the issue to their satisfaction.
Offer practical solutions, such as refunds, replacements, discounts, or credits, depending on the nature of the problem and the customer’s preferences.
Empower frontline staff to make decisions and resolve issues quickly to minimise customer frustration and inconvenience.
Follow Up and Ensure Satisfaction:
Follow up with the customer after the issue has been resolved to ensure their satisfaction and address any lingering concerns or questions they may have.
Demonstrate a commitment to their ongoing satisfaction and loyalty by checking in periodically and offering additional assistance or support as needed.
Learn and Improve:
Use feedback from unhappy customers as an opportunity to identify areas for improvement and implement corrective measures to prevent similar issues from occurring in the future.
Analyse the root causes of customer complaints, solicit feedback from frontline staff, and take proactive steps to address systemic issues or gaps in processes.
Restore Trust and Rebuild Relationship:
Take proactive steps to restore trust and rebuild the relationship with unhappy customers by exceeding their expectations and delivering exceptional service.
Offer incentives or gestures of goodwill, such as discounts, complimentary products, or personalised apologies, to demonstrate the company’s commitment to their satisfaction and loyalty.
By implementing these strategies, businesses can effectively address and resolve issues with unhappy customers, turning negative experiences into positive ones and fostering long-term satisfaction, loyalty, and advocacy.
Investing in the satisfaction and retention of unhappy customers is crucial for maintaining a positive brand reputation and sustaining growth in today’s competitive marketplace.
Types of Customer Segmentation
Customer segmentation is the process of dividing customers into distinct groups based on similar characteristics or behaviours.
Here are the four main types of customer segmentation:
Demographic Segmentation
Demographic segmentation involves dividing customers based on demographic variables such as age, gender, income, and education.
This type of segmentation helps businesses understand the unique needs and preferences of different demographic groups and tailor their marketing strategies accordingly.
For example, a clothing retailer might target younger customers with trendy styles and older customers with more classic designs.
Psychographic Segmentation
Psychographic segmentation involves grouping customers based on lifestyle, personality, values, and interests.
This type of segmentation goes beyond basic demographics to delve into the attitudes, beliefs, and motivations that drive customer behaviour.
By understanding the psychographic profiles of their customers, businesses can create more targeted and personalised marketing campaigns that resonate with their audience on a deeper level.
Behavioural Segmentation
Behavioural segmentation divides customers based on their purchasing behaviour, usage patterns, and brand loyalty.
This type of segmentation focuses on how customers interact with products or services, including their buying frequency, purchase history, and level of engagement.
By analysing behavioural data, businesses can identify different customer segments, such as loyal customers, occasional buyers, or price-sensitive shoppers, and tailor their marketing efforts to suit each segment’s preferences and needs.
Geographic Segmentation
Geographic segmentation involves segmenting customers based on their geographic location or region.
This type of segmentation recognises that customer preferences and needs can vary depending on where they are located.
Businesses may target customers in specific cities, states, or countries with localised marketing campaigns that take into account regional differences in culture, climate, and lifestyle.
For example, a restaurant chain might offer different menu items or promotions based on the preferences of customers in different geographic regions.
By leveraging these types of customer segmentation, businesses can gain deeper insights into their target audience and develop more effective marketing strategies that resonate with their customers’ unique characteristics, behaviours, and preferences.
Tailoring Strategies for Different Customer Types
The Importance of Understanding Customer Segmentation
Understanding and catering to the specific needs and preferences of different customer segments is crucial for businesses to effectively engage their target audience and drive success.
Here’s why:
Enhanced Customer Experience: By tailoring strategies to different customer segments, businesses can provide personalised experiences that resonate with each group’s unique preferences, behaviours, and motivations.
This leads to higher levels of customer satisfaction, loyalty, and retention.
Increased Relevance: By addressing the specific needs and pain points of different customer segments, businesses can ensure that their products, services, and marketing messages are relevant and impactful.
This increases the likelihood of capturing the attention of target customers and driving conversion rates.
Maximised ROI: By focusing resources and efforts on high-potential customer segments, businesses can optimise their return on investment (ROI) and allocate resources more effectively.
Tailoring strategies to specific customer segments allows businesses to prioritise initiatives that are most likely to yield positive results and drive business growth.
Competitive Advantage: Businesses that effectively cater to the specific needs and preferences of different customer segments can gain a competitive advantage by differentiating themselves in the market.
By offering tailored solutions and experiences, businesses can position themselves as industry leaders and attract a loyal customer base.
Benefits of Customer Segmentation
Customer segmentation offers several key benefits for businesses. Here are some of the main advantages:
Personalised Marketing: Tailoring Marketing Messages and Offers
One of the primary benefits of customer segmentation is the ability to personalise marketing messages and offers to specific customer segments.
By understanding the unique characteristics, preferences, and behaviours of different customer groups, businesses can create targeted and relevant marketing campaigns that resonate with their audience on a deeper level.
Personalised marketing increases the likelihood of capturing the attention of customers, driving engagement, and ultimately, improving conversion rates.
When customers feel that a brand understands their needs and preferences, they are more likely to respond positively to marketing efforts and develop stronger brand loyalty.
Improved Customer Satisfaction: Meeting the Unique Needs and Preferences
Customer segmentation enables businesses to meet the unique needs and preferences of different customer groups, leading to improved customer satisfaction.
By tailoring products, services, and experiences to specific customer segments, businesses can provide solutions that align closely with their target audience’s expectations.
This personalised approach enhances the overall customer experience, leading to higher levels of satisfaction and loyalty.
When customers feel understood and valued by a brand, they are more likely to develop long-term relationships and become advocates for the business, driving positive word-of-mouth and repeat business.
Increased Sales and Revenue: Targeting High-Value Customer Segments
Customer segmentation allows businesses to identify and target high-value customer segments with relevant products and services, leading to increased sales and revenue.
By focusing marketing efforts and resources on customers who are most likely to generate significant value for the business, businesses can optimise their return on investment (ROI) and drive growth.
Targeting high-value customer segments enables businesses to prioritise initiatives that are most likely to drive results, such as upselling, cross-selling, and retention efforts.
This strategic approach helps businesses maximise sales opportunities, increase customer lifetime value, and achieve sustainable revenue growth over time.
In summary, customer segmentation offers several key benefits for businesses, including personalised marketing, improved customer satisfaction, and increased sales and revenue.
By understanding the unique needs, preferences, and behaviours of different customer segments, businesses can create targeted strategies that drive engagement, loyalty, and profitability.
Customer segmentation is an essential tool for businesses looking to effectively engage their target audience, optimise resources, and drive long-term success in today’s competitive marketplace.
Steps to Implement Customer Segmentation
Implementing customer segmentation involves a series of steps aimed at gathering data, analysing patterns, and tailoring strategies to effectively target different customer segments.
Here’s a breakdown of the process:
Step One: Collect Customer Data
The first step in implementing customer segmentation is collecting relevant data on demographics, behaviours, and preferences.
This data can be gathered through various channels, including surveys, transactions, website interactions, social media engagement, and customer service interactions.
Collecting comprehensive data provides valuable insights into the characteristics and needs of different customer segments.
Step Two: Analyse Customer Data
Once the data is collected, businesses need to analyse it using data analytics tools to identify patterns and trends among different customer segments.
This analysis involves examining variables such as purchasing behaviour, product preferences, geographic location, and engagement level.
By uncovering patterns in the data, businesses can identify distinct customer segments and understand their unique characteristics and preferences.
Step Three: Develop Customer Profiles
Based on the analysis of customer data, businesses can develop detailed profiles for each customer segment.
These profiles should include information such as demographics, psychographics, buying behaviours, preferences, and needs.
Creating detailed customer profiles helps businesses gain a deeper understanding of each segment and tailor their marketing strategies and offerings accordingly.
Step Four: Implement Targeted Marketing Strategies
With customer profiles in hand, businesses can implement targeted marketing strategies tailored to resonate with specific customer segments.
This involves designing marketing campaigns, promotions, and messaging that address the unique needs, preferences, and pain points of each segment.
By delivering personalised and relevant marketing communications, businesses can effectively engage different customer segments and drive desired outcomes, such as increased sales, customer satisfaction, and loyalty.
By following these steps, businesses can implement customer segmentation effectively, leveraging data-driven insights to tailor strategies and offerings to different customer segments.
Implementing customer segmentation allows businesses to optimise marketing efforts, enhance customer experiences, and drive sustainable growth in today’s competitive marketplace.
Challenges and Considerations in Customer Segmentation
Implementing customer segmentation comes with its own set of challenges and considerations that businesses must address to ensure success.
Here are some key challenges and considerations:
Data Privacy and Security Concerns
One of the primary challenges businesses face when implementing customer segmentation is ensuring data privacy and security.
With the increasing focus on data protection regulations such as GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) and CCPA (California Consumer Privacy Act), businesses must comply with stringent guidelines to protect customer data.
This involves implementing robust security measures, obtaining explicit consent for data collection and processing, and ensuring transparency in how customer data is used.
Failure to address data privacy and security concerns can lead to legal consequences, damage to brand reputation, and loss of customer trust.
Integration of Data Sources
Another challenge businesses encounter is the integration of data from different sources and systems.
Customer data may be scattered across multiple platforms, including CRM systems, e-commerce platforms, social media channels, and third-party databases.
Integrating these disparate data sources can be complex and time-consuming, requiring businesses to invest in data management tools and technologies.
Additionally, inconsistencies or errors in data quality can pose challenges during the integration process, requiring careful validation and cleansing of data to ensure accuracy and reliability.
Dynamic Nature of Customer Segmentation
Customer segments are not static; they evolve and change over time in response to shifting market trends, consumer behaviours, and external factors.
Businesses must continuously monitor and analyse customer data to identify changes in customer segments and adapt their strategies accordingly.
This requires a proactive approach to segmentation, with regular updates and refinements to ensure relevance and effectiveness.
Failure to respond to changes in customer segments can result in missed opportunities, decreased effectiveness of marketing campaigns, and loss of competitive advantage.
Addressing these challenges and considerations requires a strategic approach to customer segmentation, with a focus on data governance, technology infrastructure, and agility in response to changing market dynamics.
By prioritising data privacy and security, investing in data integration capabilities, and staying agile in segmenting customers, businesses can overcome challenges and unlock the full potential of customer segmentation to drive business growth and success.
Examples of Successful Businesses Targeting Customer Segmentation
Nike: Nike effectively targets and serves various customer types by offering a wide range of products tailored to different sports, activities, and lifestyles.
From running shoes to basketball apparel, Nike caters to the specific needs and preferences of athletes and fitness enthusiasts around the world.
Amazon: Amazon utilises advanced data analytics and personalised recommendations to tailor its offerings to the preferences and behaviours of individual customers.
By analysing purchase history, browsing patterns, and demographic information, Amazon delivers personalised product recommendations and targeted marketing messages to each customer segment.
Starbucks: Starbucks caters to different customer segments by offering a diverse menu of beverages and food options to suit varying tastes and preferences.
From traditional coffee drinks to specialty lattes and teas, Starbucks provides a customisable experience that appeals to a wide range of customers, including coffee aficionados, health-conscious consumers, and on-the-go professionals.
Airbnb: Airbnb targets different customer segments by offering a variety of accommodation options to suit different travel preferences and budgets.
Whether travellers are seeking luxury villas, cozy cottages, or budget-friendly apartments, Airbnb provides a range of choices that cater to diverse needs and preferences.
These examples demonstrate how businesses can effectively target and serve various customer types by understanding their specific needs, preferences, and behaviours.
By tailoring strategies to different customer segments, businesses can create personalised experiences that drive customer satisfaction, loyalty, and business growth.
Lessons Learned and Best Practices from Effective Customer Segmentation Initiatives
Data Quality is Key: Ensuring data accuracy, completeness, and reliability is essential for effective customer segmentation.
Investing in data management tools and processes to maintain high-quality data is crucial for accurate segmentation and targeted marketing efforts.
Continuous Reassessment: Continuous analysis of customer data and market trends is necessary to identify changes in customer behaviour and preferences and adapt segmentation strategies accordingly.
Personalisation is Paramount: Personalising marketing messages, offers, and experiences based on customer segments is essential for driving engagement and satisfaction.
Tailoring communications to address the unique needs and preferences of each segment enhances relevance and effectiveness.
Integration Across Channels: Integrating customer data and insights across multiple channels and touchpoints allows businesses to deliver seamless and consistent experiences across the customer journey.
Integration enables a holistic view of the customer and facilitates targeted marketing efforts that resonate with each segment.
Experimentation and Testing: Experimentation and testing are vital for optimising segmentation strategies and identifying what resonates with each customer segment.
A/B testing, customer feedback, and analytics provide valuable insights into the effectiveness of segmentation efforts and inform future initiatives.
By learning from these examples and adopting best practices, businesses can effectively implement customer segmentation strategies to drive engagement, satisfaction, and loyalty among their target audience.
Conclusion
Customer segmentation is a powerful strategic marketing approach that enables businesses to understand, target, and serve their customers more effectively.
Throughout this discussion, we have explored the importance and benefits of customer segmentation, as well as future trends shaping its evolution.
Why You Should Invest in Customer Segmentation
Customer segmentation empowers businesses to tailor their marketing efforts to the unique needs, preferences, and behaviours of different customer segments.
By dividing customers into distinct groups based on shared characteristics, businesses can personalise marketing messages, offers, and experiences, leading to increased customer satisfaction, loyalty, and revenue.
Moreover, customer segmentation allows businesses to optimise resource allocation, improve targeting accuracy, and stay agile in response to changing market dynamics.
As competition intensifies and customer expectations continue to rise, businesses must prioritise customer segmentation as a fundamental component of their marketing strategy.
Investing in customer segmentation enables businesses to unlock valuable insights, drive personalised interactions, and differentiate themselves in a crowded marketplace.
By harnessing the power of data-driven segmentation techniques and advanced technologies, businesses can gain a competitive edge and achieve sustainable growth in the long term.
Final Thoughts on Customer Segmentation
In closing, I encourage you to explore and implement customer segmentation strategies to better target and serve your customers.
Whether you are a small startup or a multinational corporation, customer segmentation offers tremendous opportunities to optimise marketing effectiveness, enhance customer experiences, and drive business success.
Take the initiative to gather customer data, analyse insights, and develop targeted strategies that resonate with your audience.
By embracing customer segmentation as a strategic imperative, you can forge stronger connections with your customers and unlock new opportunities for growth and innovation.
Together, let’s embark on a journey to harness the power of customer segmentation and unlock the full potential of your business.
Image by Freepik
Related Reading: Customer Experience Transformation – Why it’s Important