Introduction
In the realm of strategic planning and performance management, the balanced scorecard stands as a beacon of clarity. It aligns organisational goals, metrics, and actions in a comprehensive framework.
What a Balanced Scorecard is in Business Strategy
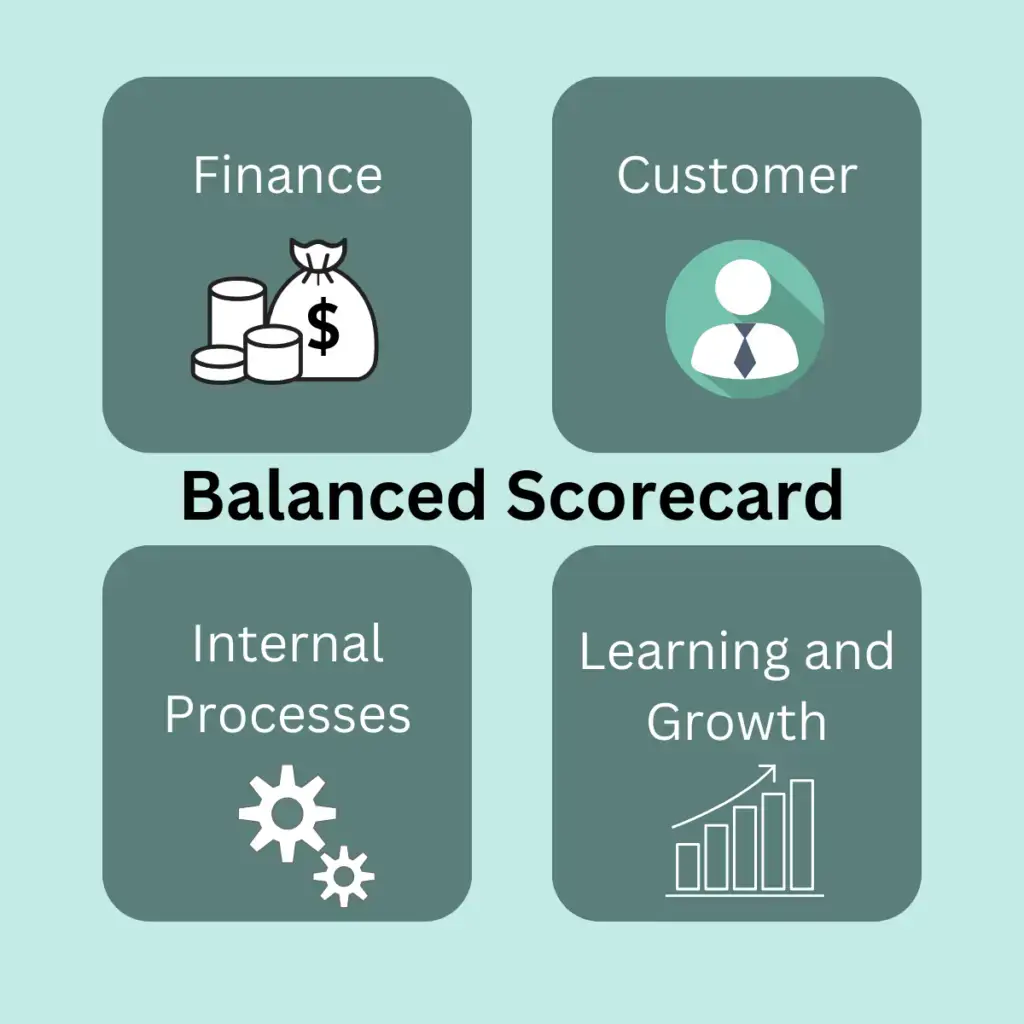
The balanced scorecard is a strategic management tool that translates an organisation’s vision and mission into a set of tangible objectives and performance metrics across four key perspectives:
- Financial
- Customer
- Internal processes
- Learning and growth.
By providing a balanced view of both financial and non-financial aspects of performance, the balanced scorecard enables organisations to monitor progress, identify areas for improvement, and align strategies with operational activities.
The Importance of Using a Balanced Scorecard for Strategic Planning and Performance Management
Utilising a balanced scorecard is paramount for effective strategic planning and performance management.
It enables organisations to go beyond traditional financial metrics and incorporate a holistic view of performance, including customer satisfaction, internal processes, and employee development.
By providing a balanced perspective, the balanced scorecard helps organisations make informed decisions, allocate resources strategically, and drive continuous improvement in both short-term and long-term objectives.
In this blog, we aim to demystify the process of creating and implementing a balanced scorecard in business strategy.
We’ll explore the key components of a balanced scorecard, discuss best practices for selecting metrics and setting targets, and provide practical guidance for aligning the balanced scorecard with organisational goals and initiatives.
Whether you’re a seasoned executive or a budding entrepreneur, this blog will equip you with the knowledge and tools needed to harness the power of the balanced scorecard in driving organisational success and sustainability.
Understanding the Balanced Scorecard Framework
The balanced scorecard framework encompasses four distinct perspectives, each representing a critical aspect of organisational performance:
Financial Perspective: The financial perspective focuses on financial objectives and outcomes that drive shareholder value and organisational sustainability.
Key metrics may include
- Revenue growth
- Profitability
- Return on investment (ROI)
- Cash flow, and
- Cost management.
The financial perspective provides insights into the organisation’s financial health, profitability, and long-term viability.
Customer Perspective: The customer perspective emphasises meeting and exceeding customer expectations to drive satisfaction, loyalty, and retention.
Metrics in this perspective may include
- Customer satisfaction scores
- Net Promoter Score (NPS)
- Customer retention rates
- Market share and
- Customer lifetime value.
By understanding and addressing customer needs and preferences, organisations can enhance customer relationships, differentiate themselves from competitors, and drive revenue growth.
Internal Processes Perspective: The internal processes perspective focuses on improving operational efficiency, quality, and innovation to deliver value to customers and stakeholders.
Key metrics may include
- Cycle time
- Process efficiency
- Product/service quality, innovation rates
- Operational cost reduction.
By optimising internal processes, organisations can streamline operations, enhance productivity, and deliver high-quality products and services in a timely manner.
Learning and Growth Perspective: The learning and growth perspective emphasises
- Developing organisational capabilities
- Knowledge
- Skills to drive innovation
- Employee engagement
- Continuous improvement.
Metrics in this perspective may include
- Employee training and development
- Employee satisfaction
- Employee turnover rates
- Knowledge sharing.
By investing in employee development, fostering a culture of learning, and promoting innovation, organisations can adapt to change, drive performance improvements, and sustain long-term success.
How Each Perspective Contributes to Achieving Organisational Goals and Objectives
Each perspective in the balanced scorecard framework plays a distinct role in contributing to the achievement of organisational goals and objectives:
Financial Perspective: Financial objectives and outcomes provide the ultimate measure of organisational performance and success.
By achieving financial targets, organisations can generate value for shareholders, sustain operations, and invest in future growth initiatives.
Customer Perspective: Satisfied and loyal customers are essential to the success of any organisation. By focusing on customer needs and delivering exceptional experiences, organisations can build strong relationships, increase customer loyalty, and drive revenue growth through repeat business and referrals.
Internal Processes Perspective: Efficient and effective internal processes enable organisations to deliver products and services that meet customer needs and expectations.
By optimising processes, reducing waste, and improving quality, organisations can enhance operational efficiency, reduce costs, and drive competitive advantage in the marketplace.
Learning and Growth Perspective: Investing in employee development and organisational capabilities is critical to fostering innovation, agility, and continuous improvement.
By empowering employees, fostering a culture of learning, and promoting knowledge sharing, organisations can adapt to change, drive innovation, and sustain long-term growth and success.
Importance of Balancing Short-term and Long-term Performance Measures
Balancing short-term and long-term performance measures is crucial for organisational success and sustainability.
While short-term measures focus on immediate outcomes and financial results, long-term measures focus on building capabilities, relationships, and competitive advantages that drive sustainable growth over time.
By balancing short-term and long-term measures, organisations can achieve a healthy mix of financial stability, customer satisfaction, operational efficiency, and innovation, positioning themselves for long-term success in a dynamic and competitive marketplace.
Step One: Identify Strategic Objectives and Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
Strategic objectives serve as the guiding principles that align organisational efforts with its overarching mission, vision, and core values.
These objectives outline the desired outcomes that the organisation aims to achieve to fulfil its purpose and realise its long-term aspirations.
Strategic objectives should be specific, actionable, and directly linked to the organisation’s strategic priorities, ensuring clarity and alignment across all levels of the organisation.
Select Relevant KPIs to Measure Progress Toward Each Strategic Objective
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) are quantifiable metrics used to measure progress toward achieving strategic objectives.
When selecting KPIs, it’s essential to consider their relevance to each strategic objective. Ensure they provide meaningful insights into performance and contribute to informed decision-making.
KPIs should be carefully chosen to reflect critical success factors, align with organisational priorities, and enable effective monitoring and evaluation of progress over time.
Ensure KPIs are Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound (SMART)
To be effective, KPIs must adhere to the SMART criteria:
Specific: KPIs should be clearly defined and focused on specific outcomes or targets related to the strategic objectives they measure.
They should leave no room for ambiguity, ensuring a shared understanding of what success looks like.
Measurable: KPIs should be quantifiable and capable of being measured using objective and reliable data.
They should provide clear indicators of progress or performance, allowing for accurate tracking and comparison over time.
Achievable: KPIs should be realistic and attainable within the organisation’s resources, capabilities, and timeframe.
Setting overly ambitious or unattainable targets can demotivate employees and undermine the credibility of the performance measurement system.
Relevant: KPIs should directly align with the strategic objectives they measure and be relevant to the organisation’s overall mission, vision, and strategic priorities.
They should focus on outcomes that have a significant impact on organisational success and contribute to value creation.
Time-bound: KPIs should be associated with a specific timeframe or deadline, establishing a sense of urgency and accountability for achieving results.
Time-bound KPIs enable organisations to monitor progress effectively and take corrective action if performance deviates from expectations.
Related Reading: How to Set Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
By defining strategic objectives aligned with the organisation’s mission, vision, and core values, selecting relevant KPIs to measure progress toward each objective, and ensuring KPIs are SMART, organisations can establish a robust performance measurement framework that drives accountability, transparency, and continuous improvement in pursuit of strategic goals.
Step Two: Develop Measures and Targets
Establish Baseline Measures For Each KPI
Before setting targets and benchmarks, it’s crucial to establish baseline measures for each Key Performance Indicator (KPI).
Baseline measures provide a starting point from which to assess current performance and track progress over time.
Baseline data can be gathered from historical performance records, industry benchmarks, market research, or internal assessments.
By establishing baseline measures, organisations can gain insights into their current performance levels and identify areas for improvement.
Set Realistic Targets and Benchmarks to Track Performance Improvement Over Time
Once baseline measures are established, organisations can set realistic targets and benchmarks to track performance improvement over time.
Targets should be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART), aligning with the organisation’s strategic objectives and KPIs.
Realistic targets take into account factors such as market conditions, resource availability, and organisational capabilities.
Benchmarks provide reference points for comparison, allowing organisations to assess their performance relative to industry standards, competitors, or best practices.
By setting realistic targets and benchmarks, organisations can create a roadmap for continuous improvement and measure progress toward strategic goals.
Align Targets with Organisational Priorities and Strategic Goals
Targets should be aligned with organisational priorities and strategic goals to ensure that performance measurement efforts contribute to overall business success.
Targets should reflect the desired outcomes and priorities outlined in the organisation’s strategic plan, mission, and vision.
By aligning targets with organisational priorities, organisations can focus resources, efforts, and initiatives on areas that have the greatest impact on achieving strategic objectives.
Aligning targets also ensures that performance measurement efforts are meaningful, relevant, and actionable, driving accountability and alignment across the organisation.
In summary, developing measures and targets involves establishing baseline measures for each KPI. It requires setting realistic targets and benchmarks to track performance improvement over time, and aligning targets with organisational priorities and strategic goals.
By taking a systematic approach to measure development and target setting, organisations can effectively monitor progress, drive continuous improvement, and achieve their strategic objectives.
Step Three: Design the Balanced Scorecard Framework
Map Strategic Objectives and KPIs to the Four Perspectives of the Balanced Scorecard
To design an effective balanced scorecard framework, it’s essential to map strategic objectives and Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) to the four perspectives:
- Financial
- Customer
- Internal processes
- Learning and growth.
Each perspective represents a distinct aspect of organisational performance, and aligning objectives and KPIs ensures a comprehensive and balanced view of performance.
Strategic objectives should be clearly defined for each perspective, outlining the desired outcomes and priorities, while KPIs provide measurable indicators of progress toward those objectives.
By mapping objectives and KPIs to the balanced scorecard perspectives, organisations can articulate their strategy, monitor performance, and drive alignment across the organisation.
Create Visual Representations, Such as Scorecard Diagrams or Dashboards, to Communicate the Framework Effectively
Visual representations, such as scorecard diagrams or dashboards, are powerful tools for communicating the balanced scorecard framework effectively.
Scorecard diagrams visually depict the relationships between strategic objectives, KPIs, and perspectives, providing a clear and intuitive overview of the framework.
Dashboards display real-time performance data in a visually appealing format, enabling stakeholders to monitor progress, identify trends, and make informed decisions.
By creating visual representations, organisations can enhance understanding, engagement, and alignment with the balanced scorecard framework, fostering transparency and accountability across the organisation.
Ensure Alignment and Integration of the Balanced Scorecard with Other Strategic Planning Processes and Systems
To maximise the impact of the balanced scorecard, it’s crucial to ensure alignment and integration with other strategic planning processes and systems.
The balanced scorecard should be integrated into the organisation’s overall strategic planning process, linking strategic objectives and KPIs to budgeting, resource allocation, and performance management activities.
Integration with existing systems, such as Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems or Business Intelligence (BI) tools, enables seamless data collection, analysis, and reporting. These all facilitate decision-making and performance improvement efforts.
By aligning and integrating the balanced scorecard with other strategic planning processes and systems, organisations can leverage synergies, streamline operations, and drive strategic alignment and execution.
In summary, designing the balanced scorecard framework involves mapping strategic objectives and KPIs to the four perspectives, creating visual representations to communicate the framework effectively, and ensuring alignment and integration with other strategic planning processes and systems.
By taking a systematic approach to design, organisations can create a powerful tool for translating strategy into action, monitoring performance, and driving organisational success.
Step Four: Implement the Balanced Scorecard
Communicate the Balanced Scorecard Framework to all Stakeholders, Including Employees, Managers, and Executives
Effective communication is key to the successful implementation of the balanced scorecard framework.
Organisations should communicate the purpose, objectives, and benefits of the balanced scorecard to all stakeholders, including employees, managers, and executives.
Clear and consistent messaging helps stakeholders understand the role of the balanced scorecard in driving strategic alignment, performance measurement, and decision-making.
Communication channels may include town hall meetings, employee newsletters, training sessions, and executive briefings, ensuring that everyone understands their role in supporting the balanced scorecard initiative and its impact on organisational success.
Provide Training and Resources to Support Understanding and Utilisation of the Balanced Scorecard
To ensure effective utilisation of the balanced scorecard, organisations should provide training and resources to stakeholders at all levels.
Training programs should cover the principles of the balanced scorecard framework, including how to interpret objectives, KPIs, and performance targets.
Resources such as user guides, tutorials, and online platforms can provide ongoing support and guidance for stakeholders as they navigate the balanced scorecard system.
By investing in training and resources, organisations empower stakeholders to effectively utilise the balanced scorecard to drive performance improvement, foster accountability, and achieve strategic goals.
Establish Processes for Data Collection, Analysis, and Reporting to Monitor Performance and Drive Decision-making
Data collection, analysis, and reporting are essential components of implementing the balanced scorecard framework.
Organisations should establish robust processes and systems for collecting relevant performance data, analysing trends, and generating actionable insights.
This may involve integrating data from multiple sources, automating data collection processes, and implementing analytical tools to support performance measurement and reporting.
Regular reporting cycles ensure that stakeholders have timely access to performance information, enabling informed decision-making, course correction, and continuous improvement.
By establishing processes for data collection, analysis, and reporting, organisations can monitor performance against strategic objectives, identify areas for improvement, and drive accountability and alignment across the organisation.
In summary, implementing the balanced scorecard requires effective communication, training, and resources to ensure understanding and utilisation of the framework by stakeholders.
Establishing processes for data collection, analysis, and reporting is essential for monitoring performance and driving decision-making based on insights derived from the balanced scorecard.
By taking a systematic approach to implementation, organisations can leverage the balanced scorecard as a powerful tool for translating strategy into action and driving organisational success.
Step Five: Monitor and Review Performance
Regularly Track Performance Against Targets and KPIs
Continuous monitoring of performance against targets and Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) is essential to ensure the effectiveness of the balanced scorecard framework.
Organisations should establish regular reporting cycles to track progress, analyse trends, and identify areas for improvement.
By regularly tracking performance, organisations can detect deviations from targets early, take corrective action, and drive performance improvement initiatives proactively.
This ongoing monitoring process provides stakeholders with real-time visibility into performance, enabling informed decision-making and accountability across the organisation.
Conduct Periodic Reviews and Evaluations of the Balanced Scorecard Framework
In addition to regular performance tracking, organisations should conduct periodic reviews and evaluations of the balanced scorecard framework itself.
These reviews provide opportunities to assess the relevance, effectiveness, and alignment of strategic objectives, KPIs, and targets with changing business priorities and market conditions.
Stakeholders should come together to review performance data, discuss insights, and identify opportunities for refinement or enhancement of the balanced scorecard framework.
Periodic reviews ensure that the balanced scorecard remains a dynamic and responsive tool for driving strategic alignment and performance improvement.
Make Adjustments and Refinements to the Framework as Needed Based on Feedback and Changing Business Conditions
Based on insights gathered from performance monitoring and periodic reviews, organisations should make adjustments and refinements to the balanced scorecard framework as needed.
This may involve updating strategic objectives, revising KPIs, setting new targets, or realigning initiatives to better reflect evolving business priorities and market dynamics.
Feedback from stakeholders, lessons learned from performance outcomes, and changes in external factors should inform decision-making about adjustments to the framework.
By making timely adjustments and refinements, organisations can ensure that the balanced scorecard remains a relevant and effective tool for driving performance and achieving strategic goals in a dynamic and competitive environment.
In summary, monitoring and reviewing performance involve regularly tracking performance against targets and KPIs, conducting periodic reviews and evaluations of the balanced scorecard framework, and making adjustments and refinements as needed based on feedback and changing business conditions.
By adopting a proactive and adaptive approach to performance management, organiations can leverage the balanced scorecard as a strategic tool for driving continuous improvement and achieving long-term success.
Benefits of Using a Balanced Scorecard
Improved Alignment of Activities with Strategic Objectives
One of the key benefits of using a balanced scorecard is improved alignment of activities with strategic objectives.
By translating strategic priorities into specific objectives and Key Performance Indicators (KPIs), the balanced scorecard provides a clear roadmap for employees at all levels to understand how their day-to-day activities contribute to the organisation’s overall goals.
This alignment ensures that resources, efforts, and initiatives are directed towards activities that drive strategic success, minimising inefficiencies and maximising organisational effectiveness.
Enhanced Performance Measurement and Accountability
The balanced scorecard facilitates enhanced performance measurement and accountability by providing a comprehensive framework for tracking progress against strategic objectives and KPIs.
By establishing clear performance targets and benchmarks, the balanced scorecard enables organisations to objectively evaluate performance, identify areas for improvement, and hold individuals and teams accountable for results.
This heightened accountability fosters a culture of performance excellence, where employees are motivated to achieve their targets and contribute to the organisation’s success.
Facilitated Communication and Transparency Across the Organisation
Another benefit of using a balanced scorecard is facilitated communication and transparency across the organisation.
By providing a common language and framework for discussing strategy and performance, the balanced scorecard enables stakeholders to communicate effectively and align their efforts towards shared goals.
Regular reporting and updates on performance metrics promote transparency, allowing stakeholders to understand the organisation’s progress, challenges, and successes.
This increased transparency fosters trust, collaboration, and engagement among employees, managers, and executives, driving organisational cohesion and effectiveness.
In summary, the balanced scorecard offers several benefits, including improved alignment of activities with strategic objectives, enhanced performance measurement and accountability, and facilitated communication and transparency across the organisation.
By leveraging these benefits, organisations can drive strategic alignment, improve performance, and achieve sustainable success in a competitive and dynamic business environment.
Case Studies or Examples
General Electric (GE): General Electric is a multinational conglomerate that has successfully implemented the balanced scorecard framework to drive strategic alignment and performance improvement across its diverse business units.
By aligning strategic objectives with financial, customer, internal processes, and learning and growth perspectives, GE has been able to track performance, identify areas for improvement, and drive operational excellence.
The balanced scorecard has enabled GE to focus on key priorities, enhance decision-making, and achieve sustainable growth in a highly competitive market.
Pfizer: Pfizer, a leading pharmaceutical company, has leveraged the balanced scorecard to align its business strategy with organisational goals and objectives.
By establishing clear strategic objectives and KPIs across financial, customer, internal processes, and learning and growth perspectives, Pfizer has been able to monitor performance, drive accountability, and foster a culture of continuous improvement.
The balanced scorecard has helped Pfizer prioritise investments, optimise resources, and deliver value to customers and stakeholders, driving long-term success in the pharmaceutical industry.
Lessons Learned and Best Practices From Their Experiences
Aligning Objectives with Strategy: Successful organisations using the balanced scorecard ensure that strategic objectives are closely aligned with the organisation’s overall strategy, mission, and vision.
By aligning objectives across financial, customer, internal processes, and learning and growth perspectives, organisations can create a unified framework for driving performance and achieving strategic goals.
Selecting Relevant KPIs: Organisations should carefully select Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) that are relevant, actionable, and aligned with strategic objectives.
By focusing on a few key metrics that truly matter, organisations can avoid information overload and ensure that resources are directed towards areas that drive the most value and impact.
Communication and Engagement: Effective communication and engagement are critical to the success of the balanced scorecard implementation.
Organisations should communicate the purpose, benefits, and expectations of the balanced scorecard to all stakeholders, fostering buy-in, ownership, and accountability at all levels of the organisation.
Continuous Improvement: Implementing the balanced scorecard is an iterative process that requires ongoing monitoring, review, and adjustment.
Successful organisations embrace a culture of continuous improvement, regularly reviewing performance data, identifying opportunities for enhancement, and making adjustments to the framework as needed to drive organisational success.
By learning from the experiences of organisations like General Electric and Pfizer, other companies can glean valuable insights and best practices for effectively implementing and leveraging the balanced scorecard to drive strategic alignment, performance improvement, and sustainable growth.
Conclusion
Throughout this blog, we’ve explored the concept of the balanced scorecard as a strategic management tool that helps you translate your vision into actionable objectives and measure performance across various perspectives.
We discussed the importance of understanding, designing, implementing, and monitoring the balanced scorecard framework to drive strategic alignment, performance improvement, and organisational success.
The balanced scorecard provides a comprehensive framework for aligning organisational goals, measuring performance, and driving continuous improvement.
By embracing the balanced scorecard methodology, you can gain clarity, focus, and direction in your strategic initiatives, fostering accountability, transparency, and agility in decision-making processes.
In conclusion, I’d encourage you to adopt a balanced scorecard approach in your strategic planning efforts to unlock the full potential of your organisation, drive performance improvement, and achieve long-term success.
By leveraging the balanced scorecard framework, you will be able to navigate challenges, capitalise on opportunities, and thrive in an ever-evolving marketplace.